
Impacted tooth is a tooth which didn’t erupt in time and it clinically and radiographically doesn’t show signs of growth. Although every tooth can be impacted, besides wisdom teeth, canines are most frequently impacted.
At age of 11 or 12, a child should have all permanent teeth except molars . Longer is the time of molar not erupting, more difficult it is to carry out a therapy. That’s why it is necessary to conduct control examinations with panoramic scanning of the upper and lower jaw after the age of 8. At that point, we observe whether all permanent teeth are present, whether there are too many teeth and whether there are bone processes which can block the growth of permanent teeth. This examination is usually done by your dentist who will instruct you to go to the orthodontist if there is a problem. Orthodontist can set a fixed appliance to make a place in a jaw for eruption of molar or some other tooth.
Impacted canine tooth
Canines are very important for harmonious look of the face because their growth affects the development of both front and side part of the jaw. They also have influence on formation of dental arch as a whole. Canines usually stay in the jaw for longest period of time and serve for anchoring and fixing artificial compensations – dentures and bridges.
The position of impacted canine is very variable. Their crown can be inclined towards palate, which is more frequent,or towards front teeth. Eruption is prevented when a canine crown, while growing out, comes across a root of lateral incisor or, in even more complicated cases, a root of central incisor. When we discover this problem on X -ray, our first thought is that , if possible, we preserve the canine because of its great importance.
If there isn’t enough room for all teeth, we usually make a place for canine by extracting the first neigbouring tooth towards back. If the canine has already endangered the other incisor with its eruption, the place for canine is obtained by extracting the above mentioned incisor for which we do not have a long – term guarantee. Later on, when canine is placed in dental arch, we use the most modern filling materials for reforming the canine crown so it looks like lateral incisor. It is done because absence of incisor has the most unfavourable effect on the face aesthetics. In cases when canine eruption has passed and irregular tooth position is detected on the X- ray, orthodontist and surgeon cooperate to solve the problem. If there is an impacted baby tooth, it is being extracted. Fixed or adjustable–appliaces are being made. Fixed appliance is better for solving these cases because we handle teeth extraction better. If the tooth is leaned towards palate, it is very difficult to pull it out with adjustable appliance. After taking an impression and an X – ray, the fixed appliance is set. It is set before surgical intervention so pulling out teeth could start immediately. Surgeon is using surgical intervention to approach the impacted tooth. Depending on its position, there are three ways to approach the tooth surgically. The surgeon releases the tooth from the bone and thus makes it possible for the othodontist to approach and glue a bracket on it and, in few sessions, lower it by pulling it down very slowly and carefully with a wire, placing it in a proper position in the dental arch.
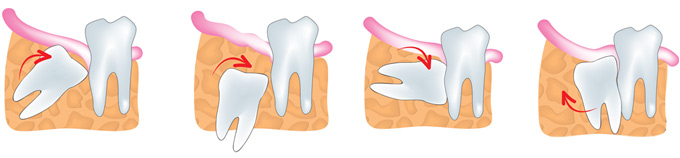
Impacted third molar
Third molars are often stuck at the end of the jaw and they can cause painful infections or other problems. They erupt between the age of 17 and 25. The area around third molar is difficult to clean which leads to bacteria multiplication causing gum diseases. In addition, oral bacteria can travel from mouth to bloodstream which then leads to possible systemic infections and illnesses that affect heart, kidneys and other organs.
Since third molars aren’t often used, they are immediately extracted if they cause problems. It is easier to extract third molars when patient is younger becuse their roots aren’t fully formed, the sorrounding bone is softer and chances for damaging surrounding nerves are smaller. Removing third molars in later age becomes more complicted because roots are fully developed ( it can affect the nerve) and a jawbone is thicker.
